(Helicoverpa armigera), (Maruca vitrata = testulalis) ,(Etiella zinckenella)
Credits: Biovision-Infonet

(c) A.M. Varela, icipe
(c) Clemson University, USDA, www.ipmimages.org

(c) GTZ-IPM Horticulture Project. Kenya
The African bollworm (Helicoverpa armigera), the legume pod borer (Maruca vitrata = testulalis) the lima bean pod borer (Etiella zinckenella) are major pests of pigeon peas in East Africa. They feed on leaves, flowers and pods, destroying them.
The African bollworm (Helicoverpa armigera)
Caterpillars are 1.5 to 4 cm long. They bore holes on pods and feed on the seeds. Usually developing in the pods and feeding partly mature seeds.
The legume pod borer (Maruca vitrata)
The adult of the legume pod borer is a moth with a wing span of 15-30 mm. It has light-brown forewings with white markings and pearly white hindwings. Though mainly nocturnal, the moth may also be seen during the day. They lay eggs in the flowers or buds, or on the pods.
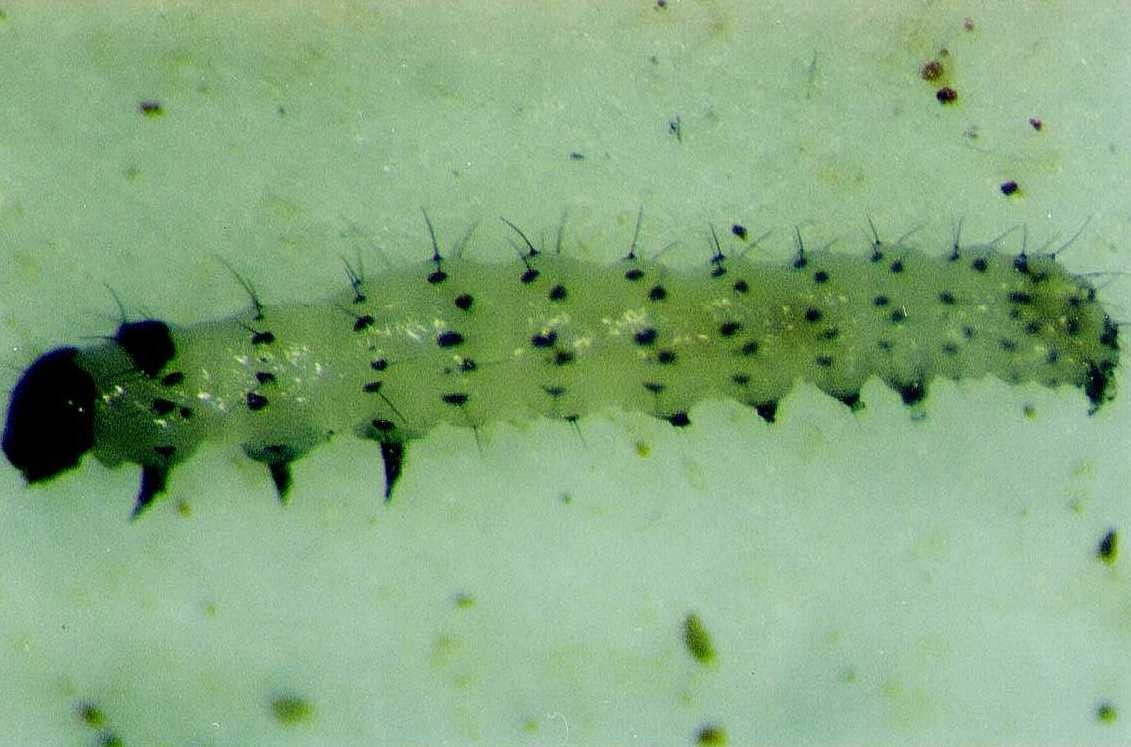
Caterpillars are whitish with black head and rows of conspicuous brown to black spots on the dorsal, lateral, and ventral surfaces of each body segment.
Fully-grown caterpillars measure about 15mm in length. They pupate in the soil. Caterpillars web leaves, flower buds and pods and feed inside the web. Flowers usually show little sign of damage until they wilt and drop.
They typically attack pods at the point of contact between two pods, or between a pod and a leaf or stem.
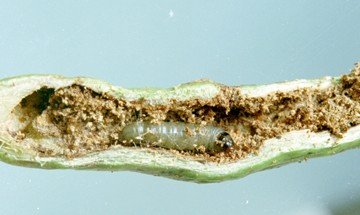
The lima bean pod borer
Adults of the lima bean pod borer are brown moths with a wing span of about 20-25 mm. They lay eggs singly or in small groups on immature pods. Young caterpillars bore into the pod.
They feed inside the pod reaching a length of 12 to 17 mm and are generally found in maturing and dried pods.
Young caterpillars are green, turning red later. Faeces in the form of granules are found inside the damaging pods.
What to do:
- Apply biopesticides such as Bt or neem products. They usually give good control of pod borers, provided they are applied to pods before the young caterpillars enter into the pods. Once the caterpillars have entered the pods they are difficult to control and by then they have caused damage. Other plant derivatives reported to control pod borers are tephrosia and chilli/garlic.
- Monitor regularly the crop to detect eggs and young caterpillars before they enter the pods
- Conserve natural enemies. Ants, parasitic wasps and pirate bugs are important in natural control. Bird perches placed just above the crop canopy are also reported to reduce the numbers of pod borers