Echinococcosis Description
Echinococcosis (hydatid disease) is a parasitic disease that affects animals and humans caused by several species of tiny tapeworms called Echinococcus
The tapeworms causing Echinococcosis are found worldwide.
Echinococcosis Animal Symptoms
Echinococcosis can affect dogs, cats, sheep, cattle, pigs, and horses
Dogs and cats are termed definitive hosts because they are NECESSARY for the survival of the parasite while the other animals (livestock) are intermediate hosts
When dogs and cats are infected they do not show any apparent signs of illness
In livestock the signs may range from no-signs to non-specific (nausea, vomiting, intermittent diarrhea, and weight loss)
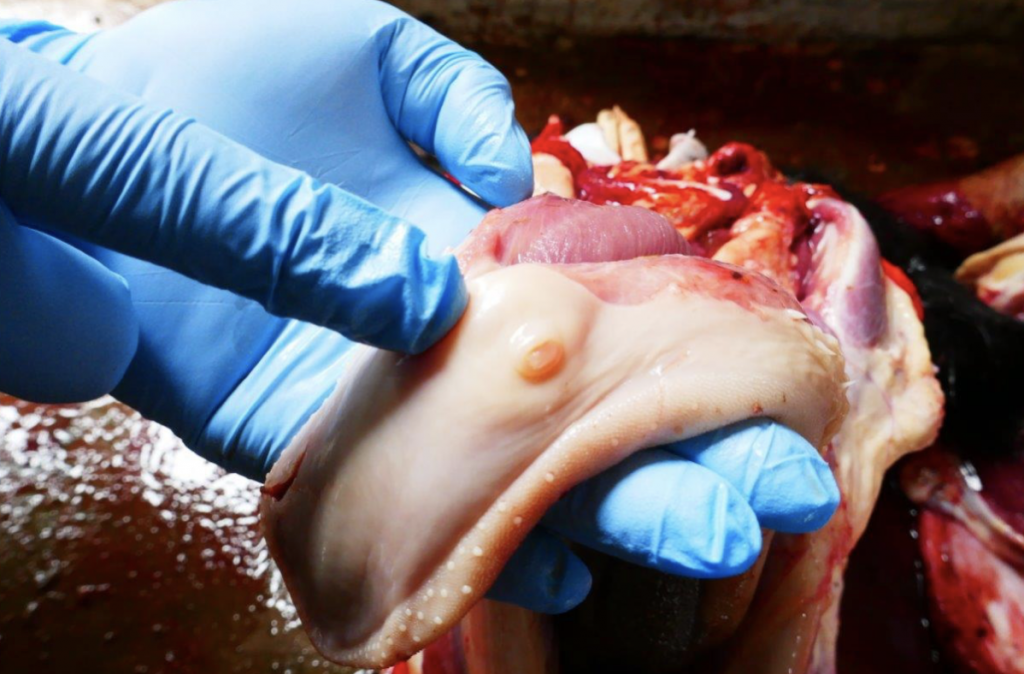
In severe livestock infestations the parasites can cause fluid or masses in the abdomen, enlargement of the liver and abdomen, and difficulty with breathing.
In livestock, reproduction and production loses occur e.g. reduced growth and milk production, reduced birth rate and losses due to condemnation of organs at PM
Severe illness in animals is exhibited by multiple cysts being found in the brain, kidneys, bones, or testes
Without control measures, infection rates can be very high in livestock, cats and dogs, with associated significant incidence in humans.
Echinococcus Animal transmission
Dogs and cats are infected by eating infected meat (meat with Echinococcus cysts) from livestock (sheep, goats, pigs and cattle)
Livestock (sheep, goats, pigs and cattle), are infected after ingesting Echinococcus eggs passed in the feces of dogs and cats
The Echinococcus eggs can survive for several months in the environment (e.g., pastures, gardens) especially in warm, moist conditions.
EchinococcusHuman Symptoms
Clinical signs in humans depend on where in the body the cyst develops, the size and number of cysts e.g. the larger the cyst the severe the symptoms
When the Echinococcus cysts are in the liver, symptoms experienced include: Abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting
When the Echinococcus cysts are in the lung (s) clinical signs include: chronic cough, chest pain and shortness of breath
Other signs depend on the location of the hydatid cysts and the pressure exerted on the surrounding tissues. Non-specific signs include anorexia, weight loss and weakness.
The severe form of the Echinococcosis occurs when multiple cysts of Echinococcus occur in the brain, kidneys, bone, or testes causing more severe illness
Echinococcus Human transmission
Humans are infected through eating contaminated food, water or soil, or through direct contact with infected faeces of livestock, dogs and cats.
Echinococcus Prevention
Preventing access of dogs to livestock carcasses or slaughter wastes from farms, households, abattoirs or butchers can help control the spread of Echinococossis
If cysts are detected at meat inspection, infected farms or communities should be targeted and control measures put in place.
Vaccinating sheep (or other livestock) to protect against the development of the larval stage of Echinococcus
Wash all fruits or vegetables thoroughly before eating them, particularly those picked in the wild or directly off the ground.
Always wash your hands with warm water and soap after handling dogs, cats and livestock
Echinococcus Action
Regularly examine and treat dogs and cats that are routinely exposed to livestock (e.g. sheep, goats, pigs and cattle)
If you suspect echinococcosis: (1) In animals – contact your veterinarian immediately; (2) In humans – contact your physician immediately
Content provided by Zoonotic and Emerging Diseases Group (ZED) University of Liverpool, International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI), Zoonoses in Livestock in Kenya (ZooLink)